
No visitors? I know the feeling!
It’s frustrating not to get traffic to your website!
Do you also want a slice of the Google pie? Then read on and learn more about Google optimization, also known as SEO!
What is SEO – also known as search engine optimization?
In Denmark, we almost exclusively use Google, so when working with SEO, it’s always focused on Google. However, there are many search engines worldwide where SEO can also be applied.
In everyday language, it’s often referred to as SEO optimization, but we’ll dive much deeper into that!
Let’s get started!
Go to Google and search!
When you search on Google, you get a series of results.
At the top, you get 4 ads, which companies pay to be displayed – the company pays per click. The same goes for the product ads you see on the right side.
These ads are managed through Google Adwords, but they have nothing to do with search engine optimization (SEO).
The other results you see on Google are what we in the industry call “organic results“. These results are not paid for by Google. They are defined by a variety of factors in Google’s algorithm.
As a rule, you should understand the following: Organic results cannot be manipulated because Google’s goal is to show the best websites at the top based on the user’s needs.
When you search for “facial care for men,” you don’t want to land on “dog food” – that’s why Google’s algorithm aims to create a connection between your website’s content and what people are searching for.
But what happens when there are 1,000,000 websites on the same topic? How can Google then determine which website should be displayed at the top?
Why is SEO important, and what does it mean to rank number 1?
Many believe that it’s unnecessary to think about Google – and many think it’s enough to focus on social media.
But that’s not how running a website works in practice.
For 95% of all webshops globally, search engines are still the most important source of traffic.
When people use Google, they are searching for a specific product or a concrete solution, so you can argue that they are receptive to a sale or advertising.
When people are on social media, they are not looking for a product, and it takes a much greater pull to convince them to buy something.
Here’s how many clicks the results on page 1 receive.
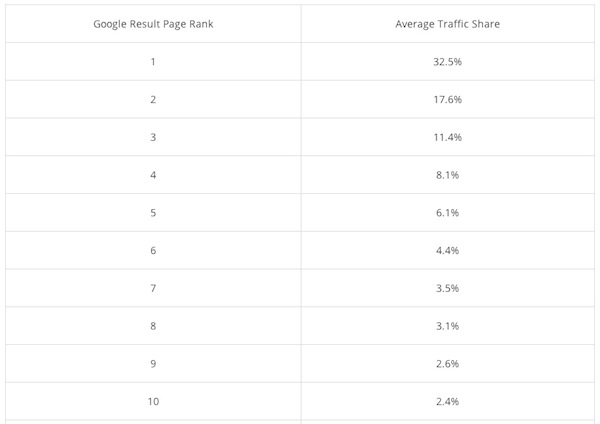
Technical SEO
One of the most challenging aspects of SEO is the technical part. Google now demands a lot from your website to ensure your users get the best possible experience.
This is something I’ve worked on the most during my 8 years as a consultant.
Since this is a crash course, I won’t take you through the entire nerdy breakdown.
Poor site structure
Does your site have a poor menu structure – is it hard for users to navigate? Google can see that. It’s frustrating for both your users and the search engines.
So make sure to create a structure that is simple and easy to navigate – it should make sense to the users. You can help yourself a bit by doing user tests and heat maps.
Where are people clicking on your website? How hard is it to find what they’re looking for?
If you have a search bar on your website, you can see what users are searching for – then you can ask yourself if it’s because they’re having trouble finding these things without a search.
If you’re struggling to run these tests, ask 5 friends or family members to use your website and watch them over their shoulders without correcting them! This way, you can get a “feeling” of whether they can figure out how to navigate your site.
Title-tag & meta descriptions
What is that?
When people search for something on Google, the first thing they see is the “title-tag” and “meta-description” – these 2 elements help users understand what your site is about and also define for Google what your site is about.
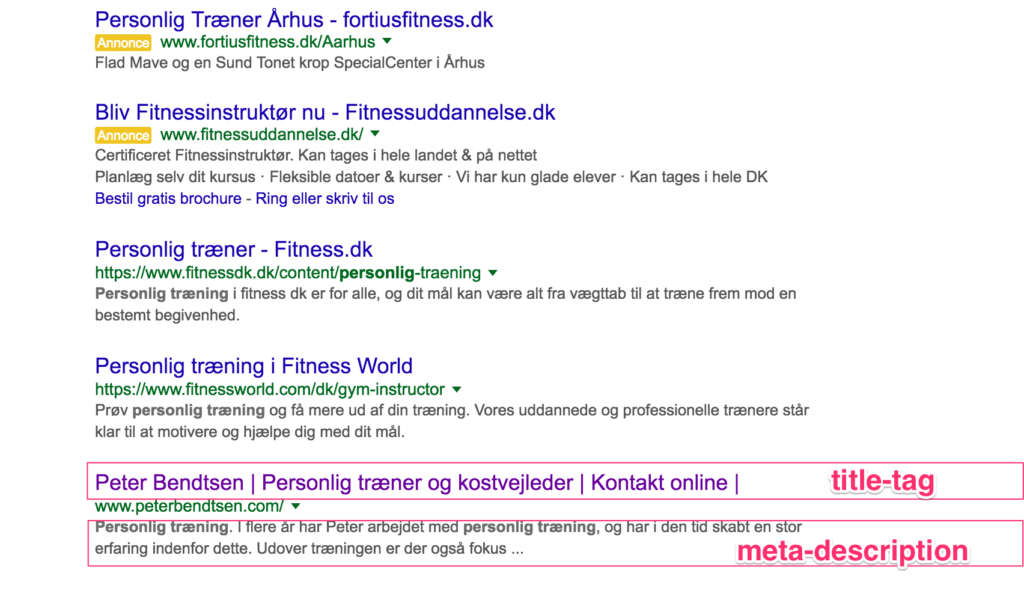 Almost any CMS (system) your website runs on will allow you to optimize the title-tag and meta-description.
Almost any CMS (system) your website runs on will allow you to optimize the title-tag and meta-description.
When we work with these at Firtal, we always focus on what people are searching for, which landing page they land on, and what that particular page converts. This is quite advanced as it requires some Excel skills to match these numbers together.
If you want to dive deep into this, I recommend reading this guide on keyword research – you can also get a lot out of using a tool called SERP tool (free) so you can see how your title-tag and meta-description look before you publish it.
If you use WordPress, install Yoast SEO, so you can easily edit these. They have a free version that works just fine.
Speed and optimization for search engines
Have you ever been on a website that is super slow?
It’s really annoying!
The more people browse via mobile phones, the more important it is for website owners to optimize their sites to make them faster.
Google also offers a tool called “pagespeed tester”
Even my website needs a tune-up – though it has been worse
When browsing on mobile, most people are on a 3G network, so a website that isn’t optimized can be really slow.
The most common culprits
- Large or too many images
- Many systems (e.g., plugins for WordPress)
- Many products per page (load time)
- Poor server (this rarely happens today)
- Lots of bad traffic from abroad pinging the server
- All content on the front page
Mobile optimization
The number of internet users browsing on mobile has exploded in recent years.
Therefore, Google places great emphasis on whether your site is mobile optimized.
Always make sure to test your website from a mobile-first perspective – which means that it’s more important for your website to function well on phones than on computers and laptops. (Of course, it should be a good experience on all devices).
You can grab your phone and test it or use Google Analytics to see which devices perform well/poorly.
You can also use Google’s mobile tester to see if you meet Google’s mobile standards.
Duplicated content – also known as duplicate content
Google rewards you for unique content – so you also get penalized if you copy text from other websites. Google wants different results in its search engine.
So write your own content – there’s a big advantage in creating great content – you have the opportunity to educate your users and get ahead in search results!
At Firtal, we have our own guides for writing the best blog posts, category texts, and product descriptions – we do everything we can to educate our people and inform them of how valuable these posts can be.
The same goes for other areas, including the use of artificial intelligence to create content, which can cause “derank”. I would also always recommend setting up Google Search Console and uploading a sitemap through it.
Internal SEO
Now that you’ve got the technical part sorted, it’s time to move on to the internal part. Imagine you run a supermarket – you’ve got the lighting, electricity, water, heating, and ventilation sorted – in other words, all the technical aspects are in place.
Now it’s time to get the products in!
Content
As described in the previous section, content means everything when it comes to ranking in Google’s organic results.
So it’s also important that you write content with care.
Let’s assume you have a site that writes about facial care for men.
It makes sense to have a page called www.made4men.dk/ansigtspleje, so this one page focuses on this topic. It’s much easier to get a website to rank higher in Google for a few words within the same category than for many words across different areas.
Examples of content
- Blog posts
- Category pages (e.g., Men’s clothing on Zalando)
- Product pages
- Guides
- FAQs
As you can see, there are plenty of opportunities to create great content that can attract traffic from Google.
Often, these texts are referred to as SEO texts.
In addition to mentioning the entire video aspect.
Links
In addition to good content, internal links also play a significant role.
Now, you shouldn’t go in and create 1000 links in every text you’ve written.
Think of it like Wikipedia – when is it relevant for the user?
For example, you can see this in my link structure in this post. When I create a link, it’s because it makes sense for what I want to convey, and thus it also benefits the user. (I hope so).
When you create links, you’re also telling Google that here is a link to a topic that has some relevance to what’s written in the text.
Additionally, you’re telling Google that you’re helping the user – and this also applies if you link out of your own website.
When I link to external sources, such as other blogs in online marketing, I don’t get anything in return from these sources.
I do it because it’s relevant to the user – and Google sees that as valuable.
H-tags
H tags aren’t particularly valuable for SEO – and yet they are!
H tags stand for “headings” – it means you define your headings just like you would in a table of contents in Word.
<h1> Main heading </h1>
<h2> Subheading</h2>
<h3>Subheading in that section</h3>
The idea of creating these sections is to tell Google what your article is about.
If you’re writing about facial care for men, your <h> tags could look like this:
<h1> Facial care for men </h1>
<h2> Great tips for facial care</h2>
<h3> Homemade face mask </h3>
The above tells Google what can be read about.
Moreover, it provides a more pleasant overview of what the page is about for the user.
The worst thing you can do is write in one long block of text.
Remember our mobile statistics from earlier?
When people are on mobile, even a short paragraph can feel incredibly long.
Image name and alt-tags
Google has become a more and more intelligent entity, but it still can’t read what’s in your images.
You can optimize this!
When you’re about to upload an image, you can rename the file.
Let’s once again assume we’re writing about facial care for men.
Suppose you upload a picture of a man taking care of his face – you can rename the file to “facialcareformen.jpg”
Once you’ve uploaded the file, you can also add an ALT tag to the image.
This means you add extra information for Google about what’s in the image – again, it could be “facial care for men”
External SEO
Now you’ve got your supermarket in order. It looks great – it’s stocked with products – the basics that drive any supermarket are in place.
What do you need now? Publicity!
Link building
Links on the web function as recommendations.
However, it doesn’t matter where the links come from.
As a rule, I divide links into 3 different categories.
Links can also harm your website – if Google suspects you’re trying to manipulate their search engine, they aren’t interested in giving you points for your efforts, and they can choose to drop your ranking or even remove you entirely from the search results!
“Random links”
When you have a website, you will occasionally get natural links. This happens, for example, when you create great content (remember the content section from earlier?), and people link to you because you have something unique to offer.
Whitehat links
When I started working with link building in 2009, we used what was called “blackhat links” – and since then, many of the strategies used back then have been categorized as blackhat today.
In other words: You must always be aware of what’s happening with Google.
Updates are constantly being rolled out that can impact your site.
Example from Searchmetrics:
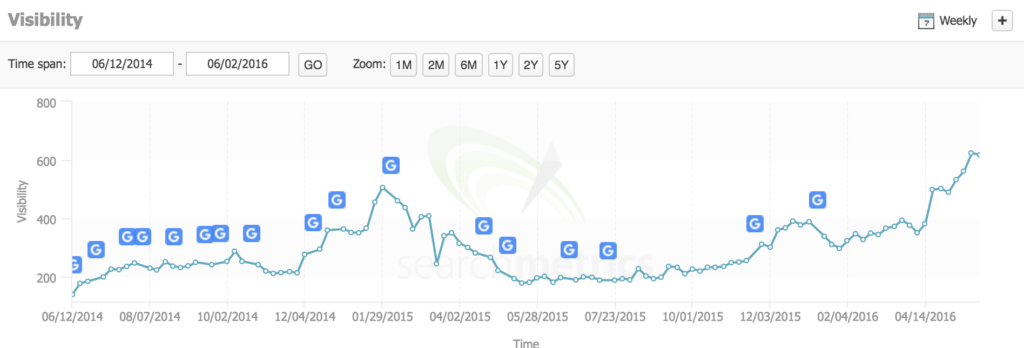 This is a graph for a company I’ve worked with. The curve reflects the visibility in Google for the site in question. The small “G’s” indicate when Google rolls out new algorithm updates.
This is a graph for a company I’ve worked with. The curve reflects the visibility in Google for the site in question. The small “G’s” indicate when Google rolls out new algorithm updates.
As you can see, these updates have significant consequences for the site’s performance. And this “penalty” from Google resulted in lost monthly revenue of over 500,000.
Therefore: Build whitehat links.
But what exactly are they?
Whitehat links are essentially links that come as naturally as possible.
Let’s look at a few examples:
- You get press coverage because you created great content or have a great product
- You get press coverage due to your expertise – like Michelle Kristensen from Good Morning TV
- You collaborate with larger companies on a cause, such as aid, and get links
- You have a new product launch that gets mentioned
- You collaborate with bloggers, companies, etc., and get mentioned (Google recently stated that links from bloggers that are bought will no longer have the same value).
The best way to get links today is through content marketing. In other words, you create something great that attracts links.
The best links are those from the most trusted sources. This could be a link from a major publication, for example, if you’ve received PR.
Additionally, you can create links to other articles that link back to you – confusing? This is called Tier2 links/link building.
Remember relevance as well! …
If you write about facial care for men, it doesn’t make much sense to get a link from a site about fishing gear.
Blackhat links
Without giving you any bad ideas – I can tell you that blackhat links worked great in the past!
You could buy 1500 links from India and fill the texts with the keyword you wanted to rank highly for – and voila, you had a number 1 position.
That’s no longer the game – so avoid these link strategies!
It can have fatal consequences for your website or the businesses you’re helping!
Analyze your results
No matter what you’re working on online, the most important parameter is > analysis!
There are countless systems for this. As a starting point, don’t be intimidated by all the tools out there.
Start with the basics – namely Google Analytics. (I promise to provide a simple beginner’s guide soon).
With Google Analytics, you can see how many visitors are coming from organic results.
This means you can constantly see if the work you’re doing is paying off.
Google Analytics is completely free and can be easily installed with a simple code that needs to be added to your website. If you use WordPress, you can also easily install one of the many plugins available for this.
Google & SEO – as of today
A lot is always happening at Google. It’s clear that the engine behind the world’s largest search engine wants to constantly optimize its algorithms to show the best possible results in search results.
The foundations of SEO optimization are still rooted in the topics mentioned above, and it’s still hard work – there are no quick fixes, especially as more and more industries experience increasingly tough competition.
That’s why we constantly see Google rolling out new updates to their algorithm.
Many of these updates have a noticeable effect across several of the clients we work with.
Update – YMYL & E-A-T
More and more people have been negatively affected by this update from Google. (YMYL – Your Money Your Life update)
There are many opinions about it, but as I see it, it’s another attempt by Google to optimize the results we get when we search for specific topics.
The challenge for Google
More and more people take Google’s answers as the truth, and it’s also difficult to navigate what’s right and what’s wrong. In principle, any content writer with some writing skills and links can get a given blog post to rank in the top 3 on Google, depending on the competition.
That’s not to say that what’s written in the post is 100% accurate, because who would qualify this?
The question is whether Google’s algorithm is on its way to becoming even stronger, for example, by crawling all studies published on a given topic and then crawling new articles and qualifying the quality based on the data.
The challenge is that if you write about finance and write something that’s untrue or directly incorrect, you have a significant impact on people’s lives. The same goes for people’s health, for example.
Google now wants to crack down (even harder) on this.
The challenge with this update is that there are no direct announcements from Google on how to optimize for it. So you can’t just optimize your speed, or the like, as we discussed in the technical aspect of optimization.
It’s about something entirely different: Who are you as a sender in the market you operate in? Who are your authors for the content you publish?

Google further states that sites in this segment require even greater credibility than others, precisely because there’s a real chance that it could affect people’s lives.

YMYL – optimization opportunities
As mentioned, Google has not issued any clear guidelines on how to avoid being hit hard by this update. Therefore, I’ve read over 50 blog posts on the subject and come up with the points I would consider addressing if your website’s content falls into the “YMYL” category or impacts people’s health.
- Ensure that the content you publish is written by real experts and not an intern who’s just scouring the internet for information.
- Ensure that the authors who write about a given topic have detailed author boxes on your site/blog posts, where they link to their credentials, for example, or their education – in other words, they must show they have expertise in the field so that their knowledge cannot be questioned.
- Make sure you don’t write anything factually incorrect, and be sure to back up your claims with relevant links out of the website. If you write about health, there are many PhD studies, etc., that could be relevant to link to.
- Don’t write content just to create affiliate sites, but to help users honestly. Don’t write to get people to buy something, but write to help people live better lives without ulterior motives. That’s what Google is all about in its raw form.
- If you allow your users to generate content, consider your disclaimers on this and make it clear to Google that it’s a community, or consider closing it off from search engines behind a login wall if many questions arise that could trigger an algorithm.
In my opinion, there’s nothing new under the sun here. Google has always tried to create real and valid search results that we as consumers can trust. It can be difficult to be critical of sources on the web – so this is another attempt by Google to ensure that the content published daily is intended to benefit people, not the opposite.
I also recommend taking a look at Google’s own guidelines, which are a good baseline to review before you start writing too much content, either on your website or elsewhere.
What does SEO cost?
If you just do a Google search on what SEO costs, you’ll get a ton of results. Unfortunately, it’s not easily answered with a single amount like other services might be. On the contrary. SEO can cost up to several million, depending on the size of the business and the complexity of the task.
Additionally, the competition in the market also influences how difficult it is to perform, and thus also what it should cost.
The most important thing when working with SEO is to have a goal in mind – what do we want to achieve?
How much can you do yourself, and how much external help do you need, such as an SEO agency or consultant?
SEO often goes hand in hand with Google Ads – you can see through your paid ads which keywords generate revenue, giving you an idea of what an SEO strategy might bring if you manage to reach the top of the search results.
If you’re not running any paid advertising on Google yet, you can use digital tools like Keyword Planner and Ahrefs to support your strategy. Here, you’ll get an idea of the volume for a given keyword and what the average CPC price is. This type of analysis is often referred to as keyword analysis.
The above is not a definitive list, but if, for example, you sell children’s clothing, be aware that it’s an extremely competitive market.
If you have a very large website that needs to be optimized technically, as we discussed in an earlier section, it can cost quite a bit, but it’s usually mapped out after a large technical SEO analysis of the website.
What is the difference between SEO and Google Ads?
As always, different results come up when you search on Google.
Some of these are through paid advertising, the service Google offers called Google Ads.
The other part is actually everything we’ve gone through above.
It’s clear that both have an impact on each other. As mentioned in the last section, you can use your data from Google Ads for your SEO optimization strategy. Similarly, after some time, you can use your SEO optimization in Google Ads.
The technical part of SEO, for example, will help you optimize your website and provide a better user experience. An improved user experience will result in a higher conversion rate – which in other words: will benefit your Google Ads – your paid advertising.
All channels interact with each other. And that’s what’s important to understand before you create a strategy – you need to consider all channels, as they all influence each other.
Another key difference is that Google Ads starts as soon as you start your ads and add a payment method. Your ads will then appear on Google.
Likewise, they stop when you turn them off.
SEO can take time, and it often does, depending on the competition in a given industry. You may not see your efforts result in increased revenue and traffic until a long period has passed.
That’s why SEO should be seen as a long-term strategy – but at the same time, it should be seen as a good initiative because it also improves the technical part of a website, which also provides a better user experience.
Conclusion
Snip Snap SEO! I hope you got something out of this introduction.
SEO must not be neglected – it’s an essential part of having a website today. We Google everything!
It takes hard work and patience to get results. It doesn’t happen overnight (unless you cheat, and then there are consequences).
Whether you’re starting a hobby blog or have an international webshop of Zalando’s size – SEO is a strategy you need to have on your to-do list.
Your turn!
What are your experiences with SEO, and have you experimented with it?










Comments